Skip to content
Skip to main menu







Your Local Community Pharmacy
Our Pharmacies all share the same vision – to provide an exceptional service for you and your family.
Knights Pharmacy Finder

Travel Health and Vaccination Services
Looking for a professional clinical service near you?
We offer a private consultation and referral service through our pharmacy clinics.

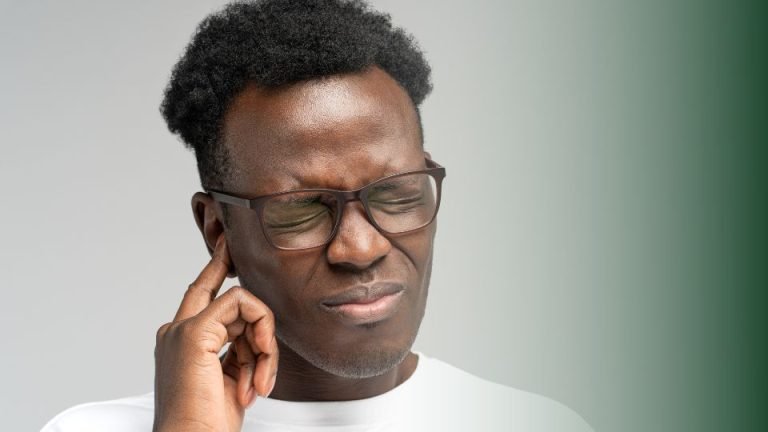
Hearing Care
If you think you might be experiencing hearing loss then take our quick, easy online hearing test now and get your results instantly.
How can we help you today?
Strengthening Communities Through Partnership
At Knights Pharmacy, we are proud to support various organisations and events through our sponsorships. These partnerships allow us to actively contribute to the betterment of communities while promoting our commitment to health and well-being.

















